
HACCP Certification Explained: Preventing Food Safety Hazards Effectively
Introduction
Food safety is a significant concern for consumers, regulators, and businesses. With increasing awareness of foodborne illnesses and contamination risks, the demand for safe, high-quality food products has never been higher. HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) certification is a globally recognized system designed to ensure food safety by identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards throughout food production. This article explores what HACCP certification is, its importance, and how it can effectively help your business prevent food safety hazards.
What Is HACCP Certification?
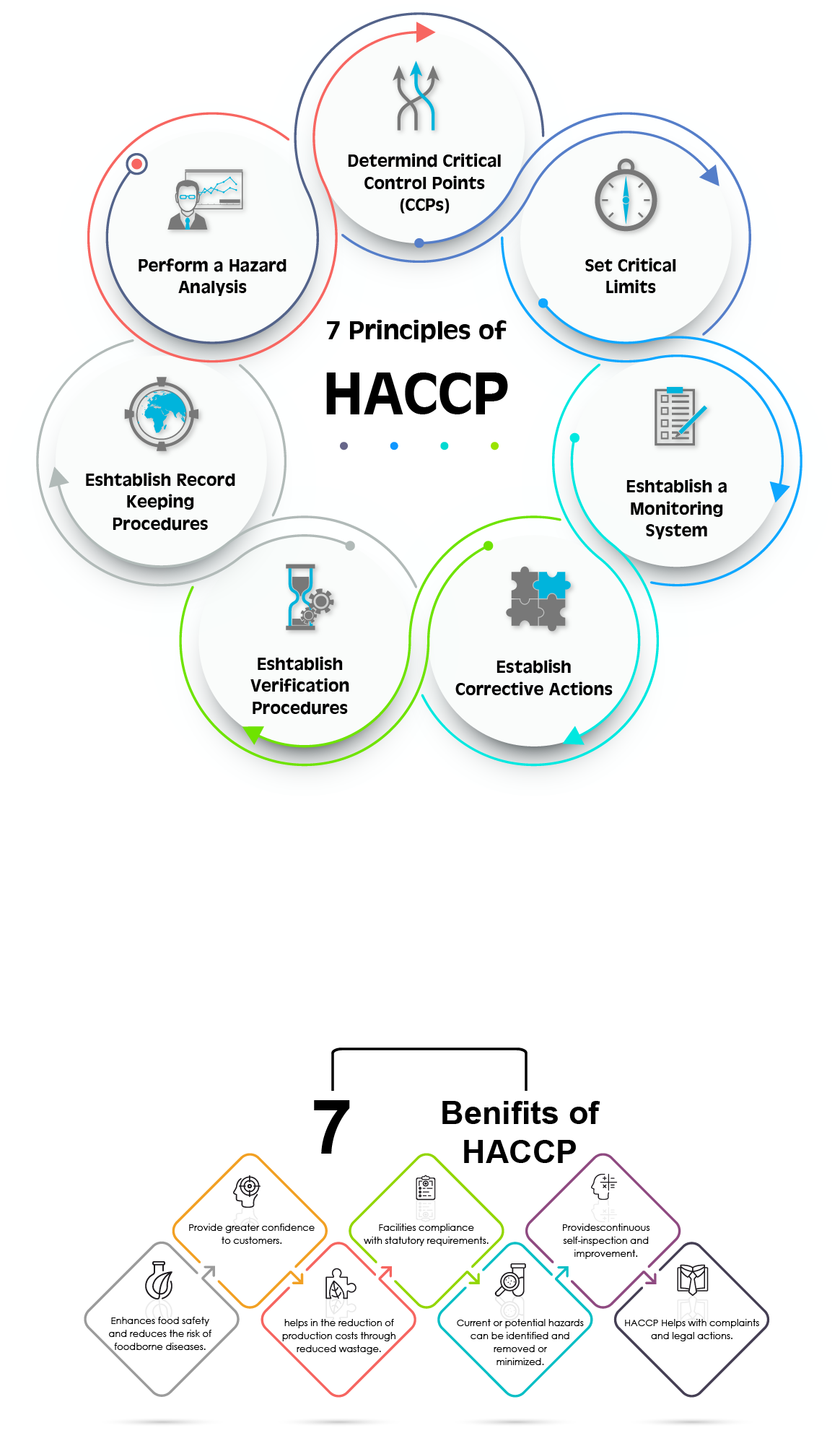
HACCP is a preventive approach to food safety. Instead of relying on end-product testing, a HACCP plan focuses on testing various stages of production. Initially conceived in the 1960s by the Pillsbury Company and NASA to keep food safe for astronauts, HACCP today is the blueprint for globalist global food safety management. One of the key principles of HACCP is the following:
➤ Conduct a Hazard Analysis: Identify potential food safety hazards and evaluate the risks associated with each part of the food production process.
➤ Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs) – Identify the steps where the potential for a food safety hazard can be removed, prevented, or reduced.
➤ Establish Critical Limits: Define safety measures for each CCP, such as, but not limited to, temperature, pH, or time measurement.
➤ Monitor the CCPs – Design steps to track and record performance at each identified CCPs.
➤ Establish Corrective Actions: Define the response if any critical limits for a control point are deviated from.
➤ Verify the System: Undertake periodic reviews and audits of the system to ensure it operates as intended.
➤ Maintain Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain compliant and verifiable records for all HACCP activities.
As verified by a certification body, HACCP certification is granted to food businesses that have established and maintained a HACCP-based food safety management system for their operations.
Impotent of HACCP Certification
1. Food Safety
With HACCP Certification, businesses can recognize and manage possible dangers, which minimizes the chance of food illnesses and tainting. WHO or World Health Organization states that unsafe food results in 600 million foodborne infections yearly, which is why HACCP systems are vital.
2. Regulatory Compliance
HACCP certification is necessary for food businesses, especially in many countries' exports and other high-risk areas such as dairy, meat, and seafood production. An example will be the U.S. FDA, which requires HACCP for seafood and juice processors, or EU regulations that require HACCP for all food processors under Regulation EC 852/2004.
3. Consumer Trust
HACCP Certification increases the consumer's mental trust, which guarantees the products purchased are safe to use and sound in quality, thus improving the brand reputation.
4. Easier Global Trade
The certification serves as an entry code to many significant business opportunities worldwide while enabling easy exporting of food products to other global markets.
5. General Business Efficiency
HACCP reduces time consumed in performing activities, thus increasing business efficiency.
Benefits of HACCP Certification
1. Eliminates Risks to Food Safety
HACCP practices focus on hazard prevention, dealing with risks such as:
● Biological Hazards: The presence of bacteria, viruses, parasites, etc.
● Chemical Hazards: Pesticides, allergens, and other toxic substances.
● Physical Hazards: Fragments of glass, metal, or plastic.
2. Decreases The Chances of Product Recalls
Early identification and control of hazards minimize the likelihood of costly, damaging recalls with HACCP.
3. Implements Increased Focus Among Employees
HACCP compliance training increases employees’ food safety knowledge, thus improving quality.
4. Facilitates Advancement
Food safety is routinely monitored and verified so that systems and processes are adapted to new technologies, risks, and challenges.
5. Improves Competitiveness in The Marketplace
Businesses become certified and gain greater competitiveness in tenders, partnerships, and consumer markets.
Steps to Achieve HACCP Certification
Getting HACCP certification requires compliance with specific standards and steps that guarantee that a company has the proper measures needed for food safety. Below is a guide to help you with the steps involved:
Step 1: Conduct a Preliminary Assessment
Before the certification process begins, businesses should analyze their current food safety management strategies and identify weaknesses and strengths that need improvement.
Step 2: Design a HACCP Plan
Formulate an encompassing HACCP plan according to the seven principles. This involves recognizing dangers, defining control points, and setting up procedures for monitoring.
Step 3: Execute the HACCP System
Incorporate training for all personnel, implement HACCP policies, and make the plan part of each day’s activities.
Step 4: Conduct Internal Audits
Regular internal audits help validate the effectiveness of the HACCP system. Any control measures that have been breached must be rectified before external audit activities.
Step 5: Undergo An External Audit
A recognized certification body will conduct the official audit to evaluate if the HACCP requirements are met.
Step 6: Get The Certification
Once the external audit has been successfully carried out, the organization will have HACCP certification, valid for a period (typically one to three years) and needs continued renewal.
Why Choose GSCS International for HACCP Certification?
When selecting a certification body, GSCS International is a trusted partner for HACCP certification. Here’s why:
- Expert Auditors: Our team comprises experienced professionals with in-depth knowledge of food safety regulations.
- Global Recognition: GSCS International certifications are widely accepted, helping businesses expand into international markets.
- Customized Solutions: Tailored HACCP certification programs designed to meet the specific needs of different industries.
- Comprehensive Training: We offer training programs to educate staff on HACCP compliance and food safety best practices.
- Continuous Support: Our experts provide ongoing guidance and support to help businesses maintain compliance.
Conclusion
HACCP certification is essential for food businesses aiming to enhance safety, improve efficiency, and comply with regulatory standards. By implementing HACCP principles, companies can effectively prevent food safety hazards, protect their brand reputation, and gain a competitive advantage.
Choosing GSCS International for your HACCP certification ensures a smooth, professional, and globally recognized process. Take the next step in securing food safety excellence—get HACCP certified today.
FAQ:
HACCP certification confirms that a business follows Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles to ensure food safety and prevent hazards.
The 7 principles include:
- Conduct hazard analysis
- Identify critical control points (CCPs)
- Establish critical limits
- Implement monitoring procedures
- Establish corrective actions
- Implement verification procedures
- Maintain documentation and records
Businesses must implement HACCP principles, train staff, follow food safety regulations, and pass an audit by an accredited certification body.
Some organizations offer free HACCP training courses, but official HACCP certification usually requires a paid audit and assessment.
The cost varies depending on business size, training, and auditing fees, typically ranging from $300 to $5,000 or more.
While training may be free, official HACCP certification requires an assessment and audit, which generally involves a fee.
