
ISO 14064 Carbon Footprint Verification for ESG & Net Zero | GSCS Intl
Carbon Footprint Verification (CFV) is a critical process that validates an organization's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through a third-party assessment. It offers a reliable and standardized method to measure emissions across operations, products, and services—helping businesses align with climate action goals, ESG frameworks, and global sustainability standards.
By quantifying emissions under recognized protocols like ISO 14064, ISO 14067, and the GHG Protocol, organizations gain accurate insights into their environmental impact and can develop credible, science-based net-zero strategies.
In this article, we explain the importance of Carbon Footprint Verification, how it works, and the advantages of partnering with a trusted verification body like GSCS International Ltd. for your emissions reporting and sustainability compliance.
As global pressure mounts for climate accountability, thousands of companies have begun their verified carbon reporting journey. Now is the time for your organization to lead in transparency and climate responsibility—with GSCS International by your side.
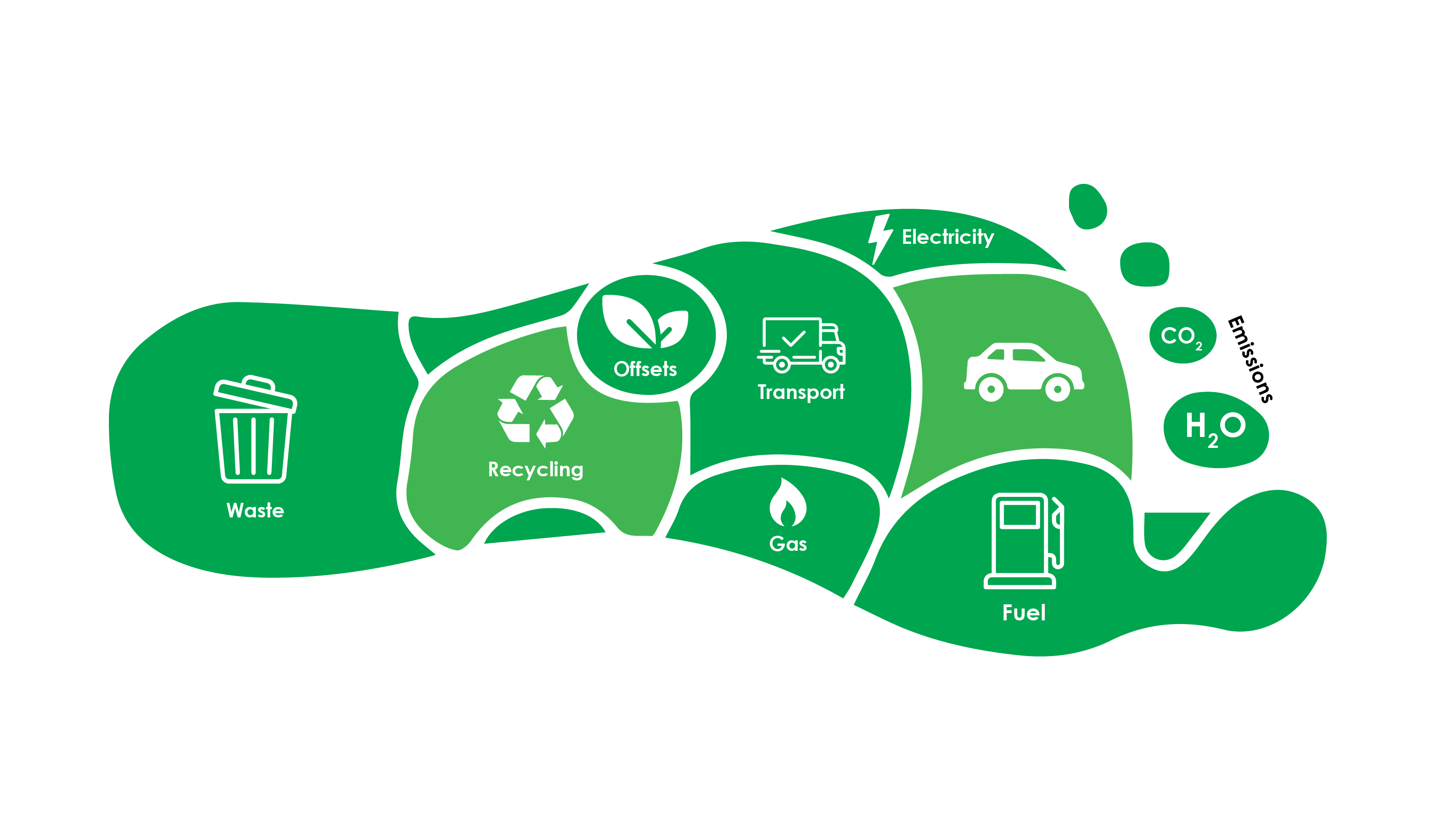
What is Carbon Footprint Verification (CFV)?
Carbon Footprint Verification (CFV) is a third-party validation process that ensures your organization’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data is accurate, complete, and aligned with international standards. It provides the credibility needed to build trust with regulators, investors, and sustainability-conscious customers.
At GSCS International Ltd., we verify your emissions inventory across:
✔ Scope 1: Direct emissions (e.g., fuel combustion, company vehicles)
✔ Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity or energy
✔ Scope 3: Other indirect emissions (e.g., supply chain, logistics, business travel)
We conduct verification under recognized frameworks including:
- ISO 14064-1 (organizational GHG emissions)
- ISO 14067 (product carbon footprint)
- GHG Protocol
- IPCC & national inventory guidelines
Why Carbon Footprint Verification is Important for Businesses
As climate regulations tighten and stakeholders demand more transparency, Carbon Footprint Verification becomes a strategic necessity. Here’s why businesses around the world are investing in third-party GHG audits:
- Compliance with Standards: CFV helps meet national and international reporting obligations (e.g., EU CSRD, SEC climate disclosures, carbon taxes).
- Transparency and Trust: Verified emissions data builds trust with stakeholders—investors, clients, and consumers—who are increasingly climate-conscious.
- Strategic Risk Management: Understanding emissions helps companies manage future risks related to carbon pricing, resource scarcity, and climate-related regulation.
- Foundation for Reduction Goals: Verification is essential before setting science-based or net-zero targets—it gives you a credible emissions baseline.
The Benefits of Carbon Footprint Verification
Companies that undergo CFV with GSCS International Ltd. enjoy the following advantages:
- Credibility and Assurance: Verified carbon data enhances your reputation by proving your environmental claims are evidence-based and accurate.
- Access to Sustainable Finance: Verification opens doors to green financing, sustainability-linked loans, and ESG investment opportunities.
- Regulatory Preparedness: CFV ensures companies are ready for emerging climate disclosure mandates and regulatory changes worldwide.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Carbon footprint assessments reveal inefficiencies in energy use and supply chains, leading to cost savings and process improvements
How to Get Carbon Footprint Verification
Step 1: Scope Definition
Decide whether you're verifying:
- Your entire organization (ISO 14064-1)
- A specific product or service (ISO 14067)
- Value chain emissions (Scope 3)
Step 2: Data Collection
Gather emissions-related data:
- Fuel & electricity consumption
- Transport & logistics logs
- Refrigerants and process emissions
- Purchased goods and travel (Scope 3)
Step 3: GHG Inventory Development
Prepare a greenhouse gas inventory report following international standards.
Step 4: Third-Party Verification
GSCS International’s certified auditors will:
- Review documentation
- Verify emission calculations
- Conduct site visits (as needed)
- Ensure completeness, accuracy, and consistency
Step 5: Verification Statement Issuance
Upon successful verification, GSCS issues a Carbon Footprint Verification Statement, suitable for:
- Sustainability reports
- ESG disclosures
- Regulatory filings
- SBTi and CDP submissions
Why Choose GSCS International Ltd. for Carbon Footprint Verification?
GSCS International Ltd. offers a seamless, trusted pathway to verified carbon reporting:
Accredited Verifier: We’re globally recognized for ISO 14064-1 & ISO 14067 verification.
Technical Expertise: Our team includes certified GHG auditors and climate consultants.
Industry Flexibility: We serve clients in manufacturing, agriculture, construction, services, and more.
Tailored Approach: We design customized verification frameworks based on your business size and emissions profile.
Training & Support: We don’t just verify—we help you understand and build internal capacity for future audits.
Conclusion:
Carbon Footprint Verification is a vital tool for any business serious about climate action. It provides the foundation for reliable emissions reduction, regulatory compliance, and leadership in sustainability. With global expectations rising, verified carbon reporting is no longer optional—it’s a competitive advantage.
Start your Carbon Footprint Verification journey with GSCS International Ltd. today—trusted by sustainability leaders worldwide.
FAQ:
A calculation estimates emissions based on available data; verification ensures the accuracy and credibility of that data through an independent audit.
Typically Scope 1 (direct), Scope 2 (purchased energy), and optionally Scope 3 (supply chain, transport, use of products).
Annually, especially if reporting to regulatory bodies or sustainability platforms like CDP.
Not always, but it is increasingly required under ESG standards, carbon taxes, and climate disclosure laws.
Energy bills, fuel usage records, GHG inventory reports, emission factors, activity data, and calculation models
